Tooth decay or an gumline cavity is a hole in the tooth which is located at the junction of the tooth and the gum. Due to the fact that this area retains the plaque build-up readily, gum line cavities may begin silently and progress rapidly. Furthermore, the procedure also increases risks when gum recession exposes more tooth surface since its cementum is soft as compared to tooth enamel.
This guide elaborates on the reasons behind the formation of cavities around the gum, early symptoms to monitor as well as the most effective treatment options. It also describes the daily habits that safeguard the gum tissue and aid in a long-term condition of the oral health.
What is a Gumline Cavity (and Why Does It Develop around the Gum Line)?
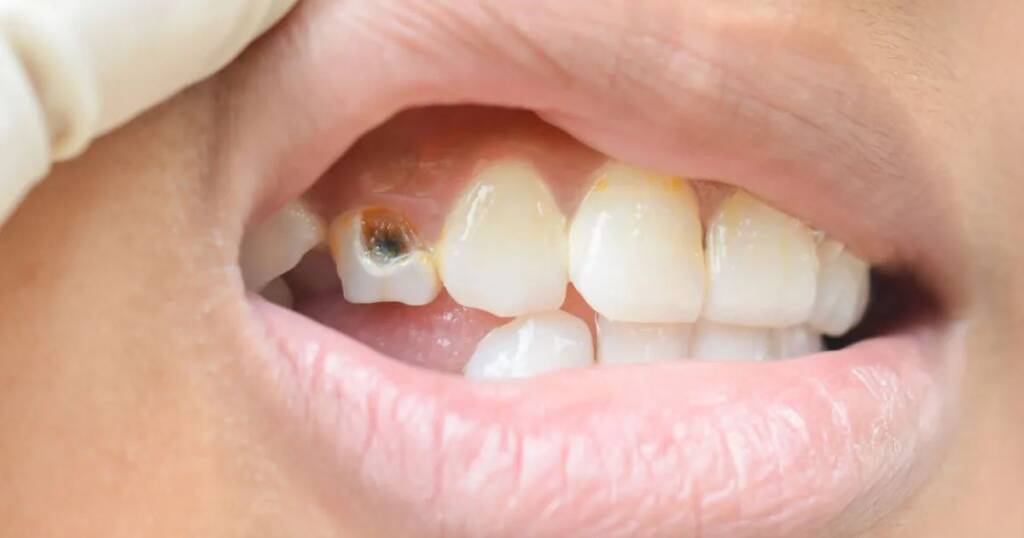
A gumline cavity is a defect on the tooth surface bordering the gum tissue which is more likely to occur at the boundary between the tooth and the gum tissue. Here food and plaque accumulate due to lack of cleaning on a hard surface particularly when one does not brush the edge or when the gums are bleeding and sore. Consequently, bacterial acid erodes enamel, and then the area destroyed enlarges.
Even though most of the gumline cavities are smooth surface cavities, they may progress to become root cavities in instances where the gums recede. Then, the breakdown will take place on an exposed root or tooth root, and it can even be more rapid than the breakdown of enamel since cementum is not as mineralized.
Comparison of gumline cavity and other cavities (in a quick comparison).
| Type of decay | Common location | Why it happens | Typical risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gumline cavity / gumline decay. | Where tooth meets gum | Plaque + difficult cleaning | Medium-high |
| Smooth surface cavities | Flat sides of teeth | Frequent snacking + plaque | Medium |
| Chewing surface cavities | Chewing surface /biting surface grooves. | Deep pits trap bacteria | Medium |
| Root cavities | Root surface below gumline | Receding gums + dry mouth | High |
What gives rise to Gum Line Cavities? (Several Factors That Raise Risk).

Cavity of the gum line is not often a result of one problem. Rather, a number of factors accumulate over the course of time and cause a greater threat of decay.
Accumulation of plaque and tartar at the gums.
When the plaque is positioned at the gumline, the bacteria consume the sugar, secrete the acids which result in the decay of the teeth. With time, tartar may develop around the plaque and the toothbrush is not able to remove it. In turn, the gum tissue of the tooth can swell, and it will be even more difficult to clean.
Sugary and acidic foods
Repeated exposures to sweet and acidic foods enhance the frequency of attack on enamel by acids. Citrus water that is healthy enough can be deemed as an acidic food in this context. Thus, it is easy to do damage by sipping with you all day long as compared to consumption of the same product in one sitting with a meal.
Common triggers near the gum:
- Energy drinks, sports drinks, soda.
- Candy, cookies, dried fruit
- Orange, fruit juice, snacks with vinegar.
- Sticky carbohydrates that stick on teeth.
Brushing aggression and gingival recession.
Vicious brushing may cause enamel to be worn out close to the gumline and may retrotract gums. In case of gum recession, there is an increased expose of root surface and decay may begin at the point where enamel has ceased to cover the tooth. Gumline decay is also common among patients who brush hard and yet still have plaque at the margin.
Dry mouth
Saliva balances the acid and cleanses bacteria. Nonetheless, dry mouth lowers such protection thus resulting in cavities developing more rapidly and expanding extensively. Drugs, oral breathing, loss of fluids and old age may all contribute hence a dentist might be using treatment of dry mouth as an important aspect of prevention.
Gum disease and chronic inflammation
Pockets and swelling are the effects of gum disease that harbour the plaque and increase the likelihood of inflammation and caries of the gums. Furthermore, persistent irritation of the gums can cause unpleasant brushing, leading to the deterioration of the quality of cleaning and the aggravation of the cycle.
Early Symptoms of a Cavity in the Gumline (What to Look and Feel for)
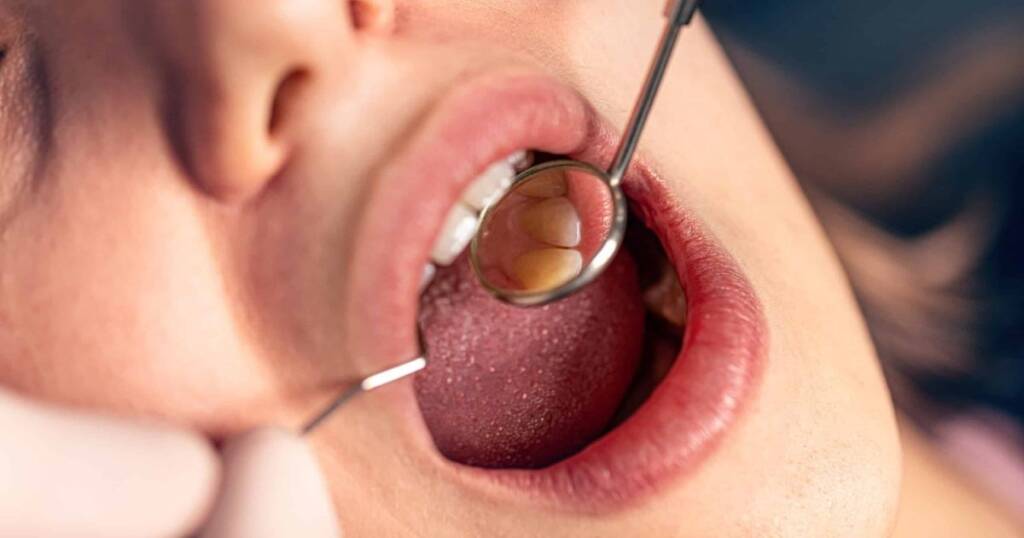
Prevention of deeper issues such as further damage below the gumline is ensured by catching a small cavities at early stages.
Visual lesions around that of the gum.
- Early demineralization (white chalky spots).
- Gumline brown or black lines.
- A notch or rough area on a smooth surface
- Food catching in one spot repeatedly
Sensations and discomfort
A cavity of the gumline may be a precursor of tooth sensitivity, particularly to cold, sweets, or hot eating. In some cases, pain will only be noted during brushing or flossing as the caries surface is flexible or the gum line is swollen.
The reasons why gumline cavities can be overlooked.
The decay may be hidden in plaque or may be located in the slightest part of the gum edge. When a hole has gone under the gum tissue, they might not be apparent on the mirror. This is the reason why regular checkups are important even in cases where there is mild or no pain.
How Fast Can Gumline Decay Get Worse if Left Untreated?

Enamel is hard, but when it is subjected to repeated acid attacks it becomes weak. The breakage of enamel allows the bacteria to reach softer layers and the cavity develops at a faster rate. Whenever the cementum is vulnerable to recession, decay may infect the entire surface of the root and result in a bigger defect than anticipated.
If left untreated, gumline cavities may lead to:
- Further decay under restorations or under the gum edge
- Chips or fractures near the neck of the tooth
- Risks of infection in case the decay is approaching the nerve.
- More complicated process and more expensive.
Treatment of Gumline Cavity (What a Dentist can Recommend)
The dentist decides the treatment that is being done depending on the location, depth and the health of the gums. In other words, treatment depends on whether the lesion is early, moderate, or deep.
1) Fluoride to harden enamel (early-stage)
In very early decay, one wants to remineralize before the process requires drilling. According to the American Dental Association, it is reported that fluoride assists in preventing tooth decay by rendering teeth more resistant to acid assaults by plaque bacterial and sugars. (ADA: https://www.ada.org/resources/research/science-and-research-institute/oral-health-topics/fluoride)
Some viable solutions can be as follows:
- Daily fluoride toothpaste
- Enhancement of enamel with fluoride varnish by professionals.
- Change of diet to lower the frequency of acid.
2) Gum line cavity dental fillings.
Once a hole is formed by a cavity, it may be filled. The dental practitioner then removes the decayed part, cleans the area then seals it with a restoration that keeps off bacteria.
Common materials:
- Composite resin (tooth-colored, bonds well)
- Dental amalgam (lasts long in there are certain cases but less attractive)
3) Dental crowns for bigger breakdown
In case of large cavity or weak teeth, dental crowns may safeguard the rest of the structure. A crown may be the best treatment when there is significant loss near the gumline or repeated filling failure.
4) root canal in case of rotting till the nerve.
Root canal can be required in case of persisting pain, severe sensitivity, or deep-seated infection, which is revealed by imaging. A crown then usually gives strength and helps to avoid fracture.
5) Minor gum surgery in cases whereby the cavity goes under the gum.
In situations where the cavity is beneath the edge of the gum and the dentist has little access, minor gum surgery can be done to enable access to the area and ensure that the dentist seals the area appropriately. This will be able to stop leakage and further damage when the cavity runs under the gum tissue.
Prevention of Gumline Cavity (Daily Oral Hygiene That Works).

Prevention aims at regulating the plaque at the gumline with the intention of safeguarding gum tissue.
Brush gently with the right technique
Brush with soft bristled toothbrush and brush the margin. Direct the bristles up to the gumline and do not scrub, instead, make short strokes as severe brushing of the gums will exacerbate the recession.
Quick checklist:
- Two minutes, twice daily
- Replace brush every 3 months
- Brush at the tooth junction not only the tops of the teeth.
Floss every day (particularly in the gum region)
Floss daily to disrupt plaque between teeth where brush bristles miss. Curve the floss into a “C” shape around the tooth and slide it slightly under the gum edge to clean near the gum without snapping.
Include fluoride and think of antibacterial mouthwash.
Use fluoride toothpaste regularly, and consult a dental health expert on the possibility of adding an antibacterial mouthwash to the treatment regimen. However, if mouthwash worsens dry mouth, a different product may work better.
Reduce sugar/acid frequency
Instead of constant grazing, keep sweeter and acidic products with the meals. After acidic foods, rinse with water and wait before brushing to avoid enamel wear.
Remove plaque before it hardens
The cleaning is done on a daily basis to prevent the plaque developing into tartar. Professional cleanings matter because tartar at the gumline keeps inflammation going and raises cavity risk.
Helpful authority resource:
- NIDCR overview of tooth decay: https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/health-info/tooth-decay.
Gumline cavity questions (Fast Answers).
Are gum line cavities smooth surface cavities?
Yes, many times, since they grow on the level tooth surface towards the gumline. But in case of recession where root structure is revealed, they can act as root cavities.
Are cavities in gumlines painful?
No. Some of them do not hurt until they rot further or induce tooth sensitivity.
Which is the most appropriate treatment of gumline cavities?
The best treatment varies. Early caries can be treated with fluoride, whereas more severe lesions can be treated with dental fillings, and severe dental problems can be treated with crowns, root canal therapy, or gum access procedures.
Major Insights: Prevent Gumline Decay to Have a Healthy Smile.
A gumline cavity begins at the place where plaque prefers to store: at the point of perception where the tooth and the gum touch. Since the gumline decays fast- not to mention receding gums or dry mouth, early detection and a proper treatment course is important. Through regular oral care, intelligent food habits, and regular dental check-ups, the gum line cavities become much easier to prevent as well as treat, saving your teeth, your gums and a healthy smile in the long run.